At Home Remedies & Medical Treatments for Receding Gums
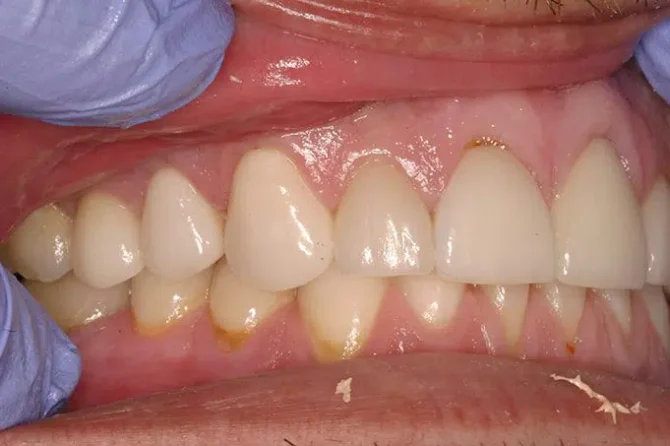
Receding gums can cause embarrassment, discomfort, and even pain. It may be difficult to tell when you have receding gums, but it is an issue that needs to be addressed as soon as possible to prevent further damage and pain. In this guide, we will discuss what receding gums are, what causes them, the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options available, and how to stop this condition from progressing. You can also find resources to use in your own research. Receding gums is a condition where the gum tissue around the teeth recedes or pulls away, exposing the root of the tooth or that part of the tooth not normally present. In addition to an aesthetically unpleasing appearance, receding gums can result in the loosening of teeth, gum infections, and other oral health problems. Fortunately, there are effective treatments available to stop receding gums and help prevent further damage.
Causes of Receding Gums
Receding gums are an increasingly common oral health condition. There are many factors that can contribute to receding gums, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, age, certain medications, and even genetics.
Poor oral hygiene is the most common cause of receding gums. When plaque builds up on the teeth and gums, it causes gum tissue to pull away from the teeth, leading to receding gums. Smoking can also weaken the gum tissue and increase the risk of receding gums. Age is another factor, as well as certain medications that can affect the health of the gums.
In some cases, genetics can also be a contributing factor to receding gums. People who have a family history of receding gums may be more likely to experience the condition themselves.
Symptoms of Receding Gums
Receding gums can be a sign that your oral health is not in the best condition. If you suspect your gums are receding, it is important to recognize the early signs and symptoms so that you can seek treatment from your dentist. Common symptoms associated with receding gums include:
- Red, inflamed gums
- Tenderness when brushing or flossing
- Bleeding when brushing or flossing
- Sensitivity when eating hot or cold food
- Increasing gaps between the teeth
- Gum recession, exposing the roots of the teeth
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, contact your dentist for a professional evaluation as soon as possible.
Diagnosing Receding Gums
Receding gums is a condition that affects many people and can lead to further oral health issues. To understand the best course of action for treatment, a dentist must first diagnose the condition. Here’s what you need to know about diagnosing receding gums.
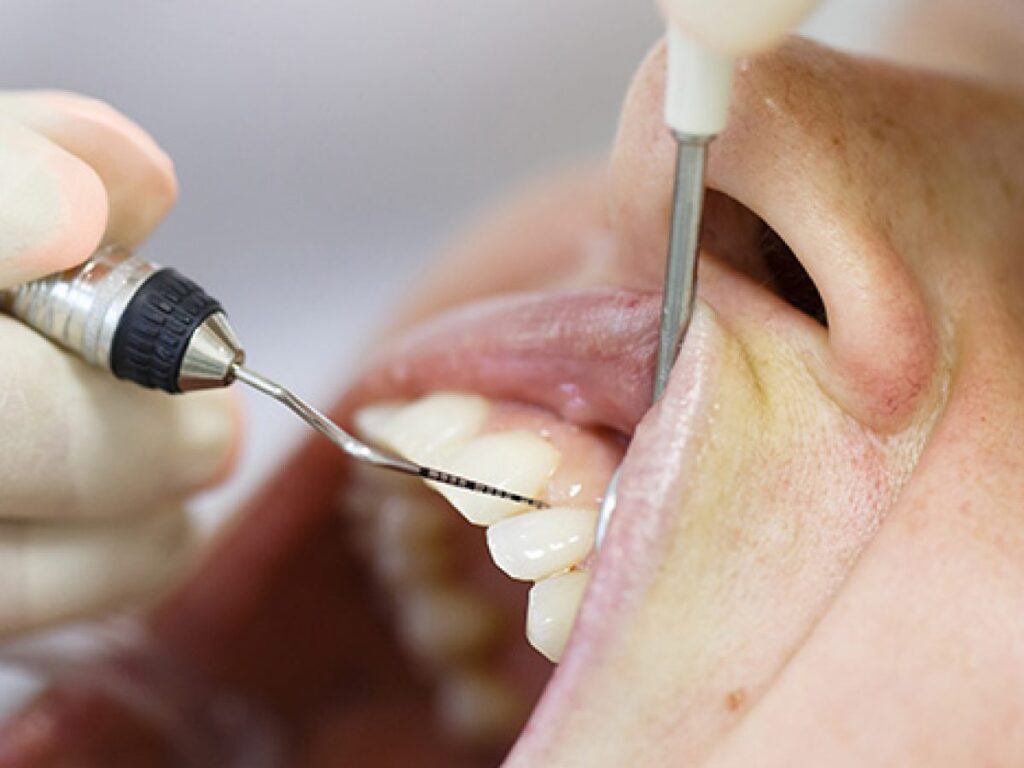
Your dentist will be able to diagnose receding gums by performing a physical examination of your mouth and teeth. During the exam, they will look for signs of gum recession, such as exposed tooth necks and widened gaps between the gums and teeth. They may also take an X-ray or measure the depth of the pockets between the teeth and gums with a probe.
Your dentist may also ask about your habits, such as how often you brush and floss and if you smoke. Your medical history may also be taken into consideration, as certain medications and existing illnesses may be connected to receding gums.
If your dentist suspects that you may have receding gums, they may take a sample from your gums to be tested for bacteria and other signs of infection. In some cases, they may refer you to a specialist if the condition is severe or requires more in-depth treatment.
Treatment Options for Receding Gums
Living with receding gums can be painful and frustrating, but the good news is that there are many treatment options available. Depending on the severity of your condition, lifestyle changes, home remedies, or medical treatments may be recommended.
Lifestyle changes can help to reduce the symptoms and slow down the progression of receding gums. These include avoiding smoking, reducing sugar consumption, maintaining a balanced diet, and practicing good oral hygiene.
Home remedies can also offer relief from some of the symptoms of receding gums. This can include brushing twice daily, flossing regularly, using an antibacterial mouthwash, and eating foods rich in vitamin C.
For more severe cases, medical treatments such as scaling and root planing, gum grafts, and laser dentistry may be needed. There are also surgical options available depending on the patient’s needs, such as pocket reduction surgery, crown lengthening, or soft tissue augmentation.
At-Home Remedies for Receding Gums
If you have receding gums, there are several things you can do at home to help manage the condition.
Brushing your teeth two times a day with a soft bristle toothbrush and a fluoride toothpaste is one of the simplest ways to keep your gums healthy. It’s important to use gentle strokes and avoid brushing too hard, as this can cause further damage to the gums.
Regular flossing is also important. Using a high-quality floss that is designed to remove plaque and bacteria between the teeth can help protect the gums from further damage.
Using an antiseptic mouthwash can also help. Rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash once or twice a day can help reduce bacteria in the mouth that can cause gum disease.
Limiting your consumption of sugary foods and beverages can help protect your gums. Sugary substances can cause bacteria to grow in the mouth, which can lead to further damage to the gums.
It’s also important to avoid tobacco products, as these can cause damage to the gums and increase your risk of developing gum disease.
Lastly, eating a balanced diet helps to ensure that your body is getting the essential nutrients it needs to maintain healthy gums. Eating foods rich in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, helps to keep the gums strong and healthy.
Medical Treatments for Receding Gums
When it comes to treating receding gums, there are several medical treatments available. These treatments can help reverse the damage done to the gums due to receding gums.
The most common medical treatments for receding gums include scaling and root planing, gum grafts, and laser dentistry.
Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is a procedure designed to remove plaque and tartar buildup from below the gum line. It helps to reduce inflammation and removes any pockets that may have formed due to gum recession. This helps to prevent further damage to the gums.
Gum Grafts
Gum grafts involve taking tissue from one area of the mouth and placing it on another area to cover exposed roots. This helps to restore the gumline and reduce the appearance of gum recession.
Laser Dentistry
Laser dentistry is a treatment that uses an intense light beam to treat gum diseases and other infections. It can be used to reduce the appearance of recession in the gums and can even help stimulate new tissue growth.
Surgery for Receding Gums
When treating receding gums, there are a variety of surgical treatments available. These include pocket reduction surgery, crown lengthening and soft tissue augmentation.
Pocket reduction surgery is a procedure in which the space between your gums and teeth, known as gum pockets, is reduced. This helps to prevent any further damage to the gums and slows down the progression of the condition.
Crown lengthening is another option for treating receding gums. This involves removing part of the jawbone so that more of the gum and tooth root is exposed. This makes it easier for bacteria to be removed from the area and also helps to reduce tooth sensitivity.
Soft tissue augmentation is a procedure in which a collagen material is injected into the gum line to help restore lost gum tissue. This can help to give your gums a fuller and more youthful appearance.
It’s important to speak to your dentist to discuss which treatment option is best for you and your individual case. Your dentist will assess your condition, take into account any risks associated with the procedures, and advise you on the most appropriate course of action.
Aftercare Following Surgery for Receding Gums
If you have had surgery to treat your receding gums, it is important to understand what you can expect during the healing period. Here are a few tips for taking care of yourself after the surgery:
- It’s normal to experience some pain and swelling in the days following the surgery. Use an over-the-counter pain reliever such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen to help reduce discomfort.
- Avoid vigorous activities such as running or playing sports for seven to 10 days after your surgery.
- Gently rinse your mouth with warm salt water twice daily. This helps to reduce swelling, encourages healing, and keeps the site clean.
- Make sure to follow your doctor’s instructions regarding any medication they may have prescribed. This typically includes an antibiotic to help prevent infection.
- Keep your mouth clean by brushing twice a day and flossing regularly.
- Avoid foods that are difficult to chew, such as chips and nuts, for at least a week after the surgery.
- Avoid alcohol, nicotine, and other substances that can irritate the surgical area.
- Schedule a follow-up appointment with your dentist to check on your progress.
Adequately taking care of yourself after surgery will help ensure the best possible results from your procedure. By following these post-operative instructions, you can help your gums heal properly and prevent any further damage.
Preventing Receding Gums
If you are worried about receding gums, there are several steps you can take to prevent it from happening. Firstly, you should brush your teeth twice a day in order to remove plaque and bacteria. In addition to this, you should floss daily in order to remove any food particles that may have become stuck in between your teeth. Secondly, it is important to avoid tobacco products, as these can cause serious gum damage. Finally, eating a balanced diet and visiting the dentist every six months for regular check-ups is also important.
Regular dental visits will help to diagnose any issues before they become more serious. Your dentist may be able to provide advice and treatments that could help to prevent receding gums. Additionally, some lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, reducing your sugar intake, and maintaining good oral hygiene can help to keep your gums healthy and stop receding gums from developing.
Conclusion
Receding gums can have a significant impact on your oral health and quality of life. Fortunately, there are steps that you can take to prevent or stop receding gums, such as brushing and flossing twice daily, using mouthwash, avoiding sugary and tobacco products, eating a balanced diet, and seeing your dentist regularly. Additionally, there are medical treatments available if you are already experiencing the effects of receding gums, such as pocket reduction surgery, crown lengthening, soft tissue augmentation, and laser dentistry. Finally, make sure to follow the aftercare instructions provided by your doctor to ensure that you heal properly.
In conclusion, it is important to take steps to prevent receding gums so that you can maintain good oral health and quality of life. Be sure to brush and floss regularly, visit your dentist every six months, and follow any aftercare instructions provided after treatment.
Resources
There is an abundance of online resources available to support those dealing with receding gums. From articles and websites to blogs and videos, they provide valuable information and advice on how to cope with the condition and take action.
Some great places to start include:
- The American Dental Association website, which has a wide range of information about oral health and receding gums.
- The National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research website, which contains detailed scientific information about gum conditions and their treatments.
- The American Academy of Periodontology website, which provides extensive resources for individuals with gum diseases.
- The Mayo Clinic website, which includes helpful advice on prevention and treatment of receding gums.
- Harvard Health Publishing, which has several articles on gum health, including information on receding gums.
In addition to these online resources, there are several books available that discuss the topic. The Mayo Clinic Guide to Oral Health and Dental Care by Dr. David G. Silverstrom and Dr. Mario Bachouros is one such book that provides comprehensive guidance.
It is important to keep in mind, however, that the information found on these websites and in books should only be used for informational purposes and should not be taken as medical advice. If you are concerned about receding gums or any other dental condition, it is best to consult a qualified dentist.
FAQs About Receding Gums
- Q: What is receding gums?
A: Receding gums is a condition in which the gum tissue around teeth begin to pull away from the teeth, exposing the sensitive root surfaces. This can often lead to pain, tooth sensitivity, and gum disease. - Q: What are the causes of receding gums?
A: The main causes behind receding gums are poor oral hygiene, smoking, age, medications, and genetics. - Q: What are the symptoms of receding gums?
A: Common symptoms of receding gums include red, swollen, and tender gums; visible roots; loose teeth; bad breath; and pain when chewing. - Q: How is receding gums diagnosed?
A: A dentist will typically diagnose receding gums through an examination of the teeth and gums and take X-rays. - Q: What treatments are available for receding gums?
A: Treatment options for receding gums include lifestyle changes, home remedies, and medical treatments, like scaling and root planing and laser dentistry. - Q: Is surgery required for receding gums?
A: Surgery is not always required for treating receding gums, however surgery may be considered a viable option depending on the severity of the condition and the desired outcome. - Q: How can receding gums be prevented?
A: You can help prevent receding gums by following good oral hygiene practices and visiting your dentist regularly. Brush at least twice a day, floss daily, avoid sugar and tobacco products, and eat a balanced diet.
