The Terrible Truth About Gingivitis: How to Spot it & Treat It
Gingivitis is a type of gum disease that affects many people around the world. It is usually caused by poor oral hygiene, but can also be linked to certain medical conditions and medications. In short, gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that results from bacteria and plaque buildup. Though it is a very common oral health problem, gingivitis is often overlooked or misdiagnosed and left untreated for too long. It is important to recognise the symptoms early so that the condition does not progress to something more serious. In this guide, we’ll go over what gingivitis is, what causes it, and how it can be managed and treated.
What Causes Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums caused by bacteria and plaque that builds up around the teeth. Poor oral hygiene is one of the main causes of gingivitis, as bacteria thrive in areas where plaque accumulates. Certain medications can also increase the risk of developing gingivitis, as they lower the body’s defenses against infection.
Other factors that may contribute to the development of gingivitis are smoking, stress, genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, and medical conditions like diabetes and HIV. Additionally, certain types of dental appliances, such as braces and crowns, can make it harder to clean the areas around the teeth, which increases the risk of developing gingivitis.
How Does Gingivitis Develop?
Gingivitis is caused by bacteria and plaque that accumulate in the gums. Plaque is a sticky substance made up of bacteria and leftover food particles that, when combined, can cause the gums to become inflamed. As this plaque builds up, it leads to an infection in the gums, which is what causes the inflammation, redness, and tenderness.
When bacteria and plaque accumulate, they release toxins into the gums, which irritate and inflame the gums. Left untreated, this can cause more severe gum diseases such as periodontitis. It is important to remember that gingivitis is reversible if caught early, so it is important to practice good oral hygiene in order to prevent it from developing.
Common Symptoms of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that can be caused by poor oral hygiene and certain medications. Once it develops, it can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms. The most common symptoms of gingivitis include:
- Redness or swelling of the gums
- Gums that are tender or painful when touched
- Bleeding from the gums during brushing or flossing
- Receding gums
- Bad breath
It’s important to note that not all gingivitis cases are the same. Some people may only experience one or two of the above symptoms while others may experience more. It is always advised to consult a dentist if any of these symptoms are experienced.
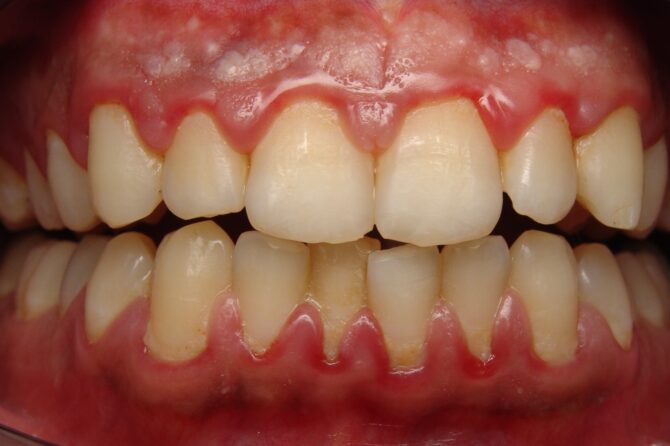
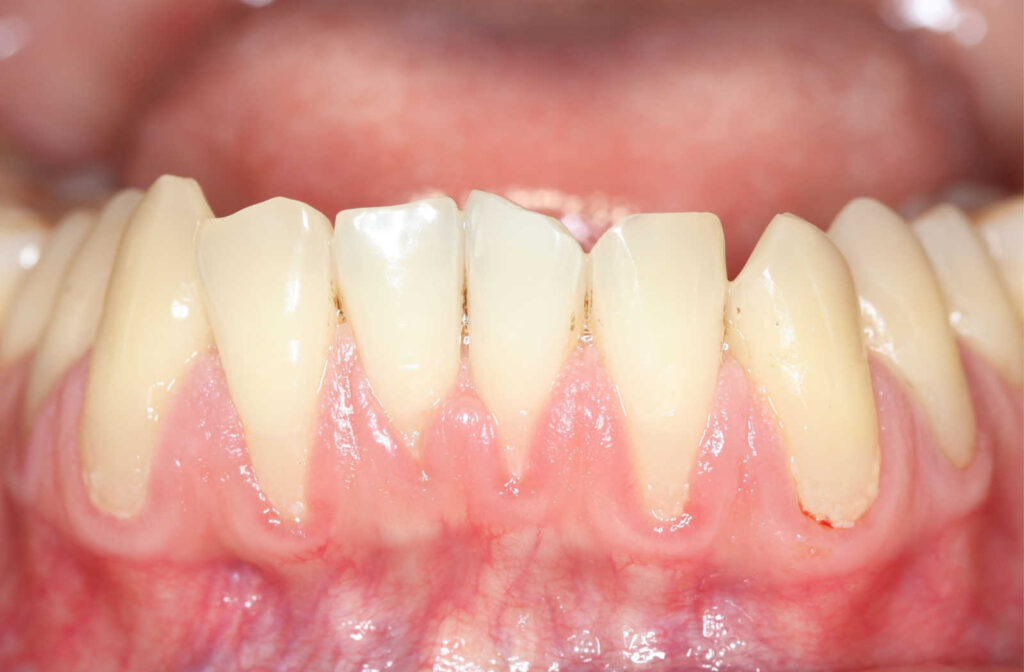
Pictures of Gingivitis
When it comes to what gingivitis looks like, there is a wide range of presentations. Generally, the signs of gingivitis are red and swollen gums that may also be tender and bleed easily when touched. In some cases, the gums may recede from the teeth, allowing for accumulation of bacteria and plaque. In more severe cases, gingivitis can lead to abscesses or infection.
It’s important to note that not everyone with gingivitis will have all of these symptoms, and the severity of the symptoms can vary from person to person. To help provide an idea of what gingivitis looks like, here are some images that depict traditional gingivitis, as well as more severe cases:
Common Complications of Gingivitis
Gingivitis left untreated can lead to more severe medical complications for the sufferer. Some of these complications include the following:
- Periodontal Disease: This occurs when plaque builds up significantly in the gums and is not removed. As a result, the gums and teeth become increasingly vulnerable to infection and progressive damage.
- Loose Teeth: As periodontal disease worsens, it can cause the gums to recede and detach from the teeth. This can lead to the teeth becoming loose and eventually needing to be extracted.
- Heart Disease: Studies have shown that the bacteria associated with gingivitis can enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation in the arteries. This, in turn, can contribute to the development of heart disease.
- Respiratory Infections: People with gingivitis may be at an increased risk of developing respiratory infections as the bacteria from the mouth can be inhaled as droplets or aerosols.
It’s important to note that these complications are rare but if left untreated, gingivitis can lead to more severe problems. Therefore, it’s important to seek help from a dentist or medical professional as soon as possible.
Treatments for Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common gum condition, and treatment options are available. Common treatments for gingivitis include medications and dental work. Depending on the severity of the condition, these treatments may be used alone or in combination to help manage symptoms.
- Medications – Anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics can be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and reduce bacterial infections.
- Dental Work – A deep cleaning, or scaling and root planing, is often needed to remove plaque and tartar build-up in the gums and teeth. The dentist may also prescribe a fluoride treatment to help protect against further damage.
In some cases, surgery may be required to remove pockets of infection from the gums. This is usually done if the plaque and tartar build-up is too severe, or if the gingivitis has become too advanced to be effectively treated with medications or scaling and root planing.
It’s important to note that gingivitis will not heal unless the underlying cause is addressed. No matter which treatments are being used, it’s essential that good oral hygiene habits are maintained to keep the gums healthy and prevent further infections.
Natural Remedies for Gingivitis
Gingivitis can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to serious pain. Fortunately, there are some natural remedies that you can use to help manage your gingivitis symptoms without having to resort to medications. Here are some of the most common natural remedies that people use to help manage their gingivitis.
- Brushing with Baking Soda: Brushing your teeth with baking soda can help reduce the swelling and inflammation in your gums caused by gingivitis. Baking soda is also known for its antiseptic properties, which can help reduce plaque accumulation and prevent further infection.
- Essential Oils: Essential oils such as tea tree oil, peppermint oil and eucalyptus oil have antibacterial and antifungal properties, which can help reduce swelling, inflammation and pain associated with gingivitis. To use essential oils for gingivitis, add a few drops of the oil to a cup of warm water and swish it around in your mouth for several minutes before spitting it out.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Hydrogen peroxide has powerful antiseptic and antiviral properties, which can help reduce the bacteria that causes gingivitis. To use hydrogen peroxide, mix it with water and swish it around your mouth for several minutes before spitting it out.
- Saltwater Rinse: Saltwater rinse can help reduce inflammation and swelling caused by gingivitis. To use saltwater, simply mix one teaspoon of salt into a cup of warm water and swish it around in your mouth for several minutes before spitting it out.
It’s important to remember that natural remedies should be used in addition to other treatments for gingivitis and should not replace regular visits to the dentist. If your gingivitis does not improve or worsens after trying these natural remedies, you should talk to your dentist about other treatment options.
Prevention Tips for Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a form of gum disease caused by bacteria and plaque that accumulates in the gums. It’s important to practice good oral hygiene habits in order to help prevent this condition from developing. Here are some key tips to help prevent gingivitis:
- Brush your teeth twice daily with a soft toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss every day to remove food particles and bacteria between your teeth and under your gums.
- Rinse your mouth with an antibacterial mouthwash.
- Limit sugary and starchy foods and beverages.
- Visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings.
By following these simple steps, you can help keep your gums healthy and reduce your risk of developing gingivitis.
Role of the Dentist in Diagnosing and Treating Gingivitis
Having a dental professional assess your gums for signs of gingivitis is essential for receiving an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. A dentist can conduct various examinations and tests to determine if you have gingivitis, including taking X-rays, performing a visual exam and inspecting saliva samples. The dentist will then recommend a treatment plan based on the severity of your condition.
The most important part of treating gingivitis is to remove the plaque and tartar that has accumulated on the teeth. Typically, the dentist will recommend trying a few different methods to remove these deposits, such as scaling and root planing, which is a deep cleaning procedure. Antibacterial mouthwash or gels may also be prescribed by the dentist to help reduce plaque and bacteria levels. In some cases, the dentist may even suggest surgery if the gingivitis is severe.
Your dentist is also the best resource for providing advice on how to properly care for your gums and prevent future infections. They will provide you with specific instructions on brushing and flossing, as well as modifying your diet for optimal oral health. They may also recommend regular visits for more thorough cleanings to help keep your gums healthy.
Tips for Managing Pain from Gingivitis
Living with gingivitis can be difficult and uncomfortable. Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to manage the pain and discomfort. Here are some tips to help you find relief from gingivitis-related pain:
- Consume an anti-inflammatory diet – Incorporate more anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, fatty fish, and fruit into your diet to help reduce inflammation in your gums.
- See your dentist regularly – Consistent visits to your dentist can help you identify any issues with your oral health and get them addressed quickly.
- Switch to a soft-bristle toothbrush – If your gums are sensitive, use a toothbrush with softer bristles to reduce the risk of causing further irritation.
- Gently floss – Flossing can help remove bacteria and food particles between your teeth, but do it gently to minimize discomfort.
- Use a mouthwash – Rinsing your mouth with an antiseptic mouthwash can kill bacteria and reduce the swelling in your gums.
You can also use over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen to help reduce inflammation and reduce the pain. However, it’s always best to talk to your doctor or dentist before taking any medication.
Conclusion
Gingivitis is one of the most common dental diseases and can affect anyone. It is important to understand the symptoms, causes and treatments available to ensure that it is managed properly. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are key to preventing further health complications.
If you experience any of the symptoms associated with gingivitis, it is important to seek professional help from a dentist or healthcare provider. They can provide personalized advice on what best to do for your condition. It is also important to practice good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing and flossing regularly, to prevent the buildup of bacteria in your mouth.
By following the tips outlined in this guide, you can help reduce your chances of developing gingivitis, and protect yourself from further health risks.
FAQs about Gingivitis
- Q: What is gingivitis?
A: Gingivitis is a form of gum disease, which is an inflammation of the gums caused by a buildup of bacteria and plaque. - Q: What causes gingivitis?
A: Poor oral hygiene, certain medications and hormones, smoking, diabetes, etc. can all be sources of gingivitis. - Q: What are the symptoms of gingivitis?
A: The main symptoms of gingivitis include red, swollen and bleeding gums. - Q: What do gingivitis and advanced periodontal disease look like?
A: Traditional gingivitis appears as red, swollen and sometimes bleeding gums, while more serious cases manifest as receded gums and exposed roots. - Q: What medical complications are associated with gingivitis?
A: Left untreated, gingivitis can lead to complications such as tooth loss and heart disease. - Q: What treatments are available for gingivitis?
A: Treatment options include medications, antibiotics and dental treatment such as scaling and root planing. - Q: Is there anything I can do at home to help manage my gingivitis?
A: Yes, you can try brushing your teeth with baking soda, brushing twice daily and using essential oils such as tea tree oil or clove oil to help reduce inflammation.
