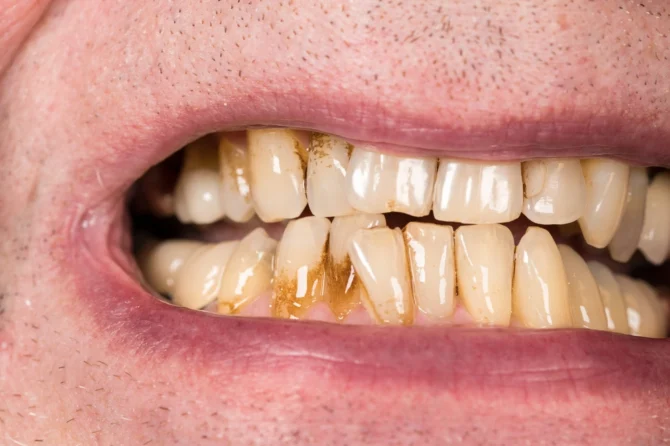
Gums Receding? Here’s How to Move Forward with Treatment
Gum Recession
Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue along the line of the teeth recedes, revealing more of the tooth than what is normal. This can happen as a result of numerous factors such as gum disease, genetics, poor dental hygiene, and grinding or clenching your teeth.
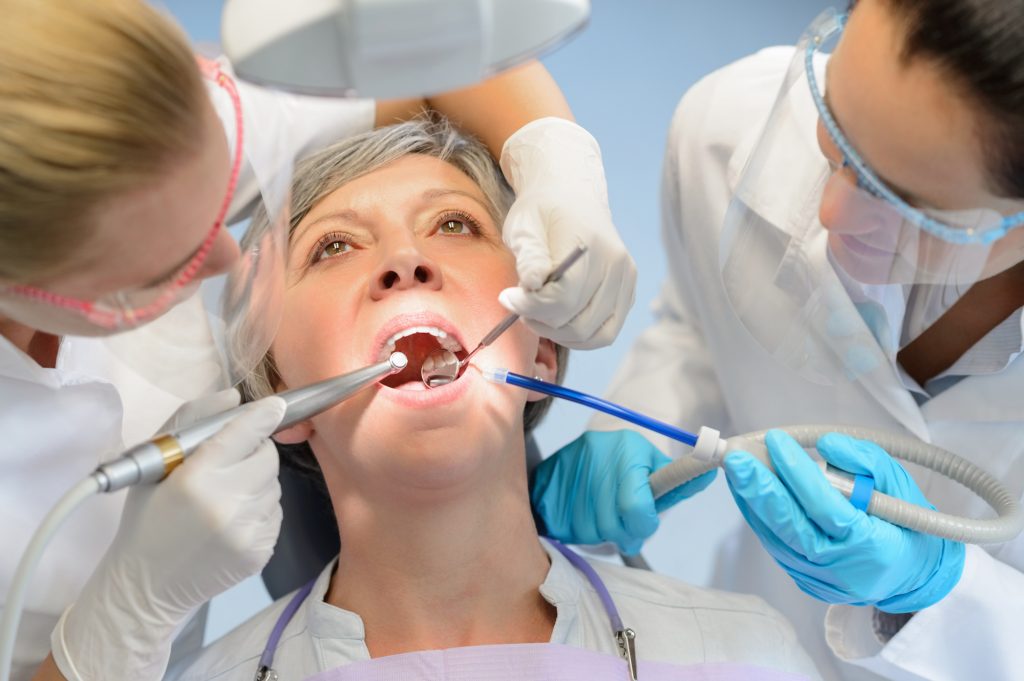
Signs & Symptoms
The most common sign of gum recession is that the gums will look longer with some of the teeth appearing to be more pointed. Other signs include:
- Tooth sensitivity to hot or cold food and drinks
- Visible roots on certain teeth
- Teeth feeling looser than usual
- Bad breath or an unpleasant taste in the mouth
Causes
There are a variety of different factors that can cause gum recession including:
- Periodontal disease – It is caused by bacteria stuck in the gums.
- Poor oral hygiene – Not brushing, flossing, or rinsing regularly can lead to bacteria buildup.
- Heavy brushing – Overly aggressive brushing can cause the gums to recede.
- Grinding or clenching teeth – If you clench or grind your teeth regularly, this can also cause gum recession.
- Genetics – Genetics play a role in some cases. Some people have naturally thinner gums.
Understanding Gum Recession Treatment Options
Gum recession is an alarming dental condition that can cause a wide range of problems if left untreated. Fortunately, there are a variety of treatments available to help address and even reverse the damage associated with receding gums. This guide will explore the different treatment options for gum recession, including medical therapies, minimally invasive surgical procedures, and preventive measures.
Medical Treatments
The first line of defense against gum disease is usually medical treatments. Various prescription medications, such as antibiotics and antiseptics, may be used to reduce inflammation, fight bacteria, and slow down the progression of gum recession. Additionally, certain vitamins and supplements, such as vitamin C, may also be recommended to boost immune system health and enhance the healing process.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive procedures, like gingivectomy and root planing and scaling, are often used to treat moderate to severe cases of gum recession. These procedures involve removing or reshaping the affected gum tissue, as well as cleaning and polishing the underlying root surfaces in order to discourage further progression of the disease.
Preventative Measures
In addition to treatments, there are also some steps you can take to reduce your risk of gum recession. Regular brushing, flossing, and rinsing with mouthwash can help remove plaque and bacteria from the affected area. Additionally, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and eating a healthy diet can also help keep your gums healthy.
By understanding the different gum recession treatment options available, you can make an informed decision about which one is right for you. Your dentist can offer advice on which treatments or preventive measures will be most beneficial in your situation.
Comparing Gingivectomy to Root Planing and Scaling
Gum recession is a common problem that affects between 10 and 12% of adults in the US. If left untreated, gum recession can lead to more severe oral health issues, such as periodontal disease. Treating gum recession often requires surgical intervention. Two popular treatment methods are gingivectomy and root planing and scaling.
A gingivectomy, also called a gum lift, is a surgical procedure which removes excess gum tissue. This procedure is used in cases of advanced gum recession, in which the gum line has receded quite far down the tooth. The procedure involves removing the excess tissue and reshaping the surrounding gum tissue to create a more even line.
Root planing and scaling, on the other hand, is a nonsurgical approach that focuses on cleaning below the gumline. During the procedure, the dentist will use both manual tools and ultrasonic scalers to remove plaque from the roots and any infected gum tissue. Root planing and scaling is usually done as part of a larger, comprehensive treatment plan.
Both procedures have their own set of benefits and drawbacks. One of the main benefits of gingivectomy is that it provides a more aesthetically pleasing result. However, it is a more invasive option and comes with potential side effects, such as bleeding, swelling, and pain. Additionally, the recovery time is typically longer than with root planing and scaling.
On the other hand, root planing and scaling is a much less invasive procedure and can be done in one appointment. It is generally well tolerated, with minimal side effects. Although the results are not as aesthetically pleasing as a gingivectomy, it does provide a long-term treatment for gum recession, as opposed to just a temporary fix.
Finally, there is a cost consideration. In general, gingivectomy tends to be more expensive than root planing and scaling. This is because gingivectomy is a surgical procedure and is often performed by a specialist while root planing and scaling is typically done by a general dentist.
Overview of Gingivoplasty and the Pinhole Surgical Technique
Gingivoplasty and the pinhole surgical technique are two gum recession treatments that involve correcting, reshaping, and recontouring the gumline. Gingivoplasty is a procedure in which the gums are cut away with a scalpel or laser and then the gumline is stitched back up. The pinhole surgical technique is a newer, minimally invasive procedure in which small pinholes are made in the gums and special tools are used to pull them down and reposition them over the teeth.
Both of these procedures have pros and cons when it comes to treating gum recession. Both can result in improved aesthetics, decreased gum recession, and reduced sensitivity. However, the recovery process for gingivoplasty can be lengthy and painful, and may involve multiple appointments. The pinhole surgical technique requires less downtime and is less painful than gingivoplasty, but the results are not as long lasting.
In terms of cost, both procedures can be quite expensive and may not be covered by insurance. It’s important to talk to your dentist to determine which procedure is best for you, and whether or not it’s something you can afford.
Treatment Tips for Successful Gum Recession Prevention
Gum recession is a common oral health issue for many people, but the good news is that it’s mostly preventable. Here are some tips to help you keep your gums healthy and prevent receding gum lines:
- Brush twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Floss every day to remove plaque and food particles from between teeth.
- Avoid aggressive brushing, as this can damage the delicate gum tissue.
- Visit your dentist regularly for checkups and maintenance cleans.
- Eat a balanced diet high in minerals and vitamins that promote healthy gums.
- Stop smoking, as smoking has been linked to gum disease.
- Reduce or eliminate sugary drinks and snacks from your diet.
- Manage stress levels, as stress can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of gum disease.
Taking these steps and following your dentist’s instructions can help keep your gums healthy and prevent receding gums. If your dentist suspects that you have gum recession, they may recommend additional treatments to prevent further damage.
Exploring Generative Treatment for Gum Recession
Gum recession is an oral health problem that is increasingly becoming more common, especially among older adults. When the gum tissue recedes, it can expose sensitive tooth root surfaces, leading to very uncomfortable and even painful symptoms. Fortunately, there are many treatments available for receding gums, including regenerative therapies.
What is Regenerative Therapy?
Regenerative therapies offer a way to restore the gum tissue back to its original size and shape through the use of minimally invasive surgical techniques. They use natural materials to help rebuild and regenerate the gums. Examples of regenerative therapies include flap surgery, gingival grafting, and periosteal elevation.
How Does Regenerative Therapy Help with Gum Recession?
Regenerative therapy can be used to not only rebuild and regenerate lost gum tissue, but also to protect the exposed tooth root. The goal of the therapy is to restore the original gum line around the teeth affected by the recession. The procedure brings healthy tissue back to the area and helps to secure the teeth from further damage.
What Are the Benefits of Regenerative Therapy?
The benefits of regenerative therapy depend on the individual patient and the severity of their gum recession. Generally, the main benefit associated with this treatment is that it helps to restore the gums to their former size and shape. This improves the appearance of the smile, prevents further damage to the tooth root, and can reduce sensitivity. Regenerative therapy is also less invasive than other gum recession treatments, making it a popular choice for many patients.
Are There Any Risks to Regenerative Therapy?
As with all medical treatments, there are certain risks associated with regenerative therapy. These risks include pain, swelling, infection, and complex healing. Patients may also develop scarring or experience changes in their bite. However, these risks can be managed and minimized with proper post-operative care and regular follow-up visits. In conclusion, regenerative therapy is a viable option for those looking to treat their gum recession. It is minimally invasive, generally has fewer risks than other treatments, and can drastically improve the appearance of the smile. However, it is important for patients to discuss all the available options with their dentist before deciding on the best treatment plan for their individual needs.
Overview of Tooth Replacement Options
When severe gum recession affects the teeth, treatments such as gingivectomy and root planing and scaling may not be enough to protect them. In cases when the teeth are beyond saving, tooth replacement options need to be considered. Depending on the extent of damage to the teeth and gums, different tooth replacement options may be recommended.
The most common tooth replacement options include dental bridges, dentures, and dental implants. Dental bridges are an excellent choice for replacing one or more missing teeth. Unlike dentures and implants, a bridge is a non-removable appliance and it looks and feels just like natural teeth. Bridges can be either fixed in place by means of crowns or they can be removable and require regular cleaning.
Dentures are also a popular choice for replacing missing teeth. They consist of a frame that supports one or more false teeth, which sit on top of the gums. Dentures are removable, so they can be taken out easily and cleaned. For patients with severely receded gums, dentures may be the only option as they do not require any surgery.
Dental implants are a more permanent solution, as they involve surgically inserting titanium posts into the jawbone. Once installed, these posts act as anchors for artificial teeth, providing a secure and natural-looking replacement for missing teeth. Implants can last for a lifetime with proper care, making them a great long-term solution for severe gum recession.
Regardless of which tooth replacement option is chosen, it is important to seek professional advice before deciding on a treatment plan. A qualified dentist or periodontist can assess the condition of the teeth and gums and recommend the best course of action.
Conclusion
Gum recession is a common yet serious dental issue that, if left untreated, can lead to major complications including tooth loss. In this guide, we reviewed the signs and symptoms of gum recession, treatment options, and preventive measures. We compared gingivectomy with root planing and scaling, explored the merits of gingivoplasty and the pinhole surgical technique, and discussed how regenerative treatments can help with gum recession. Lastly, we reviewed tooth replacement options for severe cases of gum recession.
When it comes to treating gum recession, prevention is key. Regular brushing and flossing, avoiding bad habits such as smoking and using tobacco products, and visiting your dentist regularly can all help reduce the risk of receding gums. If you think you may have gum recession, don’t hesitate to speak to your dentist; they can provide information on the best treatment options for you.
We hope this guide has been helpful in better understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gum recession. With the right care, gum recession doesn’t have to rule your life.
FAQ’s About Gum Recession Treatment
- Q: What is gum recession?
A: Gum recession is a condition characterized by the loss of gum tissue along the gum line of the teeth, exposing more of the root surface. It can cause sensitivity, tooth decay, and tooth loss if left untreated. - Q: What are the signs and symptoms of gum recession?
A: Common signs and symptoms of gum recession include sensitive teeth, a long tooth appearance, receding gums, and visible root surfaces. - Q: What are some medical treatment options for gum recession?
A: Medical treatments for gum recession can include deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup, antibiotics to fight infection, and mouth rinses and toothpaste for extra protection. - Q: What is the difference between gingivectomy and root planing and scaling?
A: Gingivectomy is a surgical procedure to remove and reshape gum tissue. Root planing and scaling is a nonsurgical cleaning procedure to remove bacteria and debris. Both have similar recovery times and costs. - Q: How does regenerative therapy help with gum recession?
A: Regenerative therapies such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and tissue engineering can help stimulate the body’s natural healing process and promote the growth of new gums. - Q: What kind of tooth replacement options are available?
A: Tooth replacement options include dental bridges, dental implants, partial dentures, and full dentures. The type of tooth replacement depends on the degree of gum recession. - Q: What tips can I follow to reduce my risk of gum recession?
A: Tips for reducing your risk of gum recession include brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, using a fluoride mouthwash, avoiding tobacco use, and visiting your dentist regularly.
